Hi Everyone!! This article will share Land and Soil Questions & Answers.
In my previous posts, I have shared Land and Soil Objective Type Questions & Answers and Resources Questions & Answers so, make sure to check these posts as well.
Land and Soil Questions & Answers
Question 1: What are the factors that affect the land use?
Answer: The factors that affect the land use are:
- Physical factors such as soil, topography, minerals, climate and availability of water.
- Human factors such as population density, availability of capital and technology.
Question 2: How is soil formed?
Answer: Soil is formed as a result of physical, chemical and biological weathering of rocks which breaks the rock into smaller particles with sizes ranging from boulders to grains. These particles then mix with organic matter such as vegetable remains and remains of dead animals and insects. The biological action of the bacteria then causes decay in the soil giving rise to humus. It is this humus that gives a dark brown colour to the soil.
Question 3: Name any four methods used to conserve land.
Answer: Afforestation, land reclamation, regular use of pesticides and fertilizers, planting of shelter belts and avoiding overgrazing are some of the common methods used to conserve land.
Question 4: What is Land Degradation? List the various factors of land degradation.
Answer: Land degradation refers to the decline in productivity of cultivable land or forest land.
The various factors that lead to land degradation are:
- It results from the unscientific use of land because of the increased pressure of meeting the demand of an ever-growing population.
- Excessive exploitation of land occurs due to various human activities such as intensive farming, deforestation, using fertile land for settlements, practicing shifting cultivation, mining sites, etc. These activities may result in degradation of land; soil erosion and desertification. All such phenomena lead to the fast depletion of natural resources and ecological imbalance.
Question 5: How are human activities responsible for soil exhaustion?
Answer: Soil exhaustion is the deterioration of mineral nutrients in the soil. Human activities such as overcropping, multi-cropping, shifting agriculture, deforestation, dry farming, over-irrigation and overgrazing lead to soil exhaustion thereby giving rise to poor soil.
Land and Soil Questions & Answers
Question 6: How does the crop rotation help the land?
Answer: Crop rotation ensures that different crops are grown in different times of the year and utilises different mineral nutrients from the soil. This ensures the land recharge its fertility.
Question 7: Differentiate between Contour Bunding and Contour Farming.
Answer:
- Contour bunding involves construction of banks along the contours across the hill slopes, with the help of rocks to collect water and prevent soil erosion.
- Contour farming is ploughing of field along the contours of the slope to avoid soil erosion.
Question 8: Define the following.
(a) Mulching
Answer: Mulching is covering the soil with hay or dry grass, between two plants so as to retain its moisture and prevent soil erosion.
(b) Plugging
Answer: Plugging is choking of gullies with rocks to prevent the flow of water and soil erosion.
(c) Situ soil
Answer: When soil remains at the place of its origin, it is called residual or in situ soil.
Question 9: What are various methods of land conservation?
Answer: Afforestation, land reclamation, regulated use of pesticides and fertilizers, planting of shelter belts and avoiding overgrazing are various methods of land conservation.
Question 10: Describe soil profile with the help of a diagram.
Answer: Soil is the uppermost thin layer of the Earth made up of tiny loose material originated from fine rock material and decayed organic matter. Soil is formed by a slow process. It takes thousands of years to make a soil layer of 5 to 7 cm.
Soil Profile:
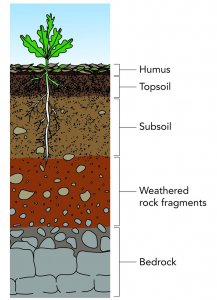
Humus – It is the uppermost layer of the top soil that contains organic matter from the decay of dead plants and animals.
Topsoil – It is the topmost layer of the soil, consisting of fine rock materials such as clay, silt, sand, etc. and mineral matter. It is frequently subjected to leaching. Roots of plants are confined to this layer.
Subsoil – It is made up of weathered rock and soluble minerals. Rain water is collected here.
Substratum – It consists of weathered rock material also known as regolith.
Bedrock – It is the bottom rock layer, made up of solid unweathered parent rock.
Land and Soil Questions & Answers
Question 11: What measures can be taken to check soil erosion?
Answer: Measures that can be taken to check soil erosion are:
1. Shelter Beds – These are made in coastal or dry regions where rows of tall trees are planted around the farms to act as wind break and check soil erosion.
2. Afforestation – It is done for checking spread of the desert and checking soil erosion.
3. Contour Farming – It is ploughing of field along the contours of the slope to avoid soil erosion.
4. Contour Bunding – It involves the construction of banks along the contours across the hill slopes, with the help of rocks to collect water and prevent soil erosion.
5. Plugging – It is choking of gullies with rocks to prevent the flow of water and soil erosion.
Question 12: Give reasons:
(a) We should conserve soil.
Answer: We should conserve soil because soil is the foundation of plant life. It also supports animal life. Moreover, it is necessary for water supply.
(b) Parent rock is important in soil formation.
Answer: Parent rock is important in soil formation because it gives colour, texture, chemical composition, mineral content and permeability to the soil. For example – erosion of sandstone gives rise to sandy soil and basalt gives rise to black soil in arid regions.
Question 13: Differentiate between sheet erosion and gully erosion.
Answer:
- Sheet erosion generally takes place on a sloping land after heavy rainfall and is relatively even erosion of a layer of soil without channel formation.
- Gully erosion is the formation of deep grooves caused by heavy rainfall, giving rise to ravines or badlands.
Question 14: Define the following terms:
(a) Soil
Answer: Soil is the uppermost thin layer of the Earth made up of tiny loose material originated from fine rock material and decayed organic matter.
(b) Land degradation
Answer: It refers to the decline in productivity of cultivable land or forest land.
(c) Soil erosion
Answer: It refers to the removal of the topsoil by various agents of gradation, causing loss to soil fertility.
(d) Land use
Answer: The term ‘land use’ suggests different uses of land made by humans.
(e) Soil exhaustion
Answer: It is the deterioration of mineral nutrients in the soil because of poor farming techniques such as overcropping, multi-cropping, shifting agriculture, deforestation, dry farming, overgrazing and over-irrigation.
Question 15: State with examples how soil types are classified.
Answer: Soil type is classified on the basis of its colour, texture and formation. If soil remains at the place of its origin, it is called residual or in situ soil. If it gets deposited elsewhere by the action of wind, water or glacier, it is called transported soil.
Question 16: Prove how the rate of weathering is governed by climatic conditions.
Answer: Climatic conditions such as temperature and rainfall govern the rate and the type of weathering. For example, chemical weathering is prominent in the areas of high rainfall and monsoon climate. Decomposition of organic matter is rapid in humid climate.
So, these were Land and Soil Questions & Answers.